Setup Guide ODG

Project Setup for Android Studio
This guide uses Android Studio, if for some reason you can't use Android Studio yet, please refer to the guide below on how to setup an Eclipse project. Please note that Eclipse support is deprecated with Wikitude SDK 5.0 release and won't be supported in future versions.
Create a new Android Application Project (There is also a working SampleProject bundled in this SDK, where all these steps are already made)
Copy the file
libs/wikitudesdk.aarinto the libs folder of your module. (project root/app/libs)Open
build.gradlefrom your module, add thewikitudesdk.aaras a dependency and tell gradle to search the libs folder, like in the code below.
android {
...
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
compile (name: 'wikitudesdk', ext:'aar')
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:21.0.3'
}
repositories {
flatDir{
dirs 'libs'
}
}
- If you already purchased a license, please set the applicationId to the package name you provided us with.
defaultConfig {
applicationId "xxxx"
}
- Add the following permissions to your AndroidManifest.xml
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_GPS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.location" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.sensor.accelerometer" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.sensor.compass" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:glEsVersion="0x00020000" android:required="true" />
<uses-sdk android:targetSdkVersion="19" android:minSdkVersion="9"/>
- The activity holding the AR-View (called
wearableArchitectViewin the following) must have setandroid:configChanges="screenSize|orientation"in theAndroidManifest.xml, for example this could look like:
<activity android:name="com.yourcompany.yourapp.YourArActivity"
android:configChanges="screenSize|orientation"/>
- Enter a valid trial license key. Read this chapter on how to obtain a free trial key.
Project Setup Eclipse
Please note that Eclipse support is deprecated with Wikitude SDK 5.0 release and won't be supported in future versions.
- Create a new Android Application Project (There is also a working SampleProject bundled in this SDK, where all these steps are already made)
- Create a
libsfolders in your project root directory and copylibs/wikitudesdk.jar In Eclipse enter
Preferences->Android->Buildand ensure the optionForce error when external jars contain native librariesis unchecked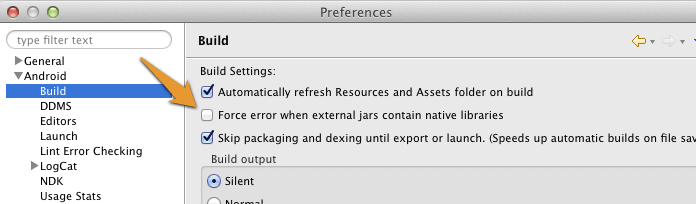
Add the following permissions to your Manifest.xml
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_GPS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.location" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.sensor.accelerometer" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.sensor.compass" android:required="true" />
<uses-feature android:glEsVersion="0x00020000" android:required="true" />
<uses-sdk android:targetSdkVersion="19" android:minSdkVersion="9"/>
- The activity holding the AR-View (called
wearableArchitectViewin the following) must have setandroid:configChanges="screenSize|orientation"in theAndroidManifest.xml, for example this could look like:
<activity android:name="com.yourcompany.yourapp.YourArActivity"
android:configChanges="screenSize|orientation"/>
- Enter a valid trial license key. Read this chapter on how to obtain a free trial key.
AR View in Activity
Keep in mind that the Wikitude SDK is not a native Android SDK as you know from other SDK's. The basic concept is to add an wearableArchitectView to your project and notify it about lifecycle events. The wearableArchitectView creates a camera surface and handles sensor events.
The experience itself, sometime referred to as ARchitect World, is implemented in JavaScript and packaged in your application's asset-folder (as in this project) or on your own server.
The experiences are written in HTML and JavaScript and call methods in Wikitude's AR-namespace (e.g. AR.GeoObject).
You have to include
<script src="https://wikitude.com/libs/architect.js"></script>
in your HTML files to use the AR namespace and the wearableArchitectView will handle them properly. To test an ARchitect World on a desktop browser, you must include ade.js tool instead to avoid JavaScript errors and see a development console.
It is recommended to handle your augmented reality experience in a separate Activity.
Declare the wearableArchitectView inside a layout XML.
E.g. Add this within FrameLayout's parent tags.
<com.wikitude.architect.WearableArchitectView android:id="@+id/wearableArchitectView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"/>
WearableArchitectView is creating a camera surface so ensure to properly release the camera in case you're using it somewhere else in your application.
Besides a camera (front or back-facing) the WearableArchitectView also makes use of compass and accelerometer values, requires OpenGL 2.0 and at least Android 4.0.
WearableArchitectView.isDeviceSupported(Context context) checks whether the current device has all required hard- and software in place or not.
It is very important to notify the WearableArchitectView about life-cycle events of the Activity.
Call wearableArchitectView's onCreate(), onPostCreate(), onPause(), onResume(), onDestroy() inside your Activity's lifecycle methods.
Best practice is to define a member variable for the wearableArchitectView in your Activity. Set it right after setContentViewin Activity's onCreate(), and then access wearableArchitectView via member-variable later on.
this.wearableArchitectView = (WearableArchitectView)this.findViewById( R.id.wearableArchitectView );
final ArchitectStartupConfiguration config = new ArchitectStartupConfiguration();
config.setLicenseKey( * license key */ );
this.wearableArchitectView.onCreate( config );
wearableArchitectView.onCreate( config ).
Activity's onPostCreate() is the best place to load the AR experience.
this.wearableArchitectView.onPostCreate();
this.wearableArchitectView.load( "YOUR-AR-URL" );
On the first start of an AR-View the Wikitude Epson SDK looks for a calibration. By default the calibration is stored on the external storage, it can also be set manually by calling wearableArchitectView.onPostCreate('calibration path'). It is recommended to use the default calibration path so users who have other apps installed powered by Wikitude SDK can use the same calibration. More about the calibration and how it can be customized can be found here.
The wearableArchitectView.load() argument is the path to the html file that defines your AR experience. It can be relative to the asset folder root or a web-url (starting with http:// or https://).
e.g. wearableArchitectView.load('arexperience.html') opens the html in your project's assets-folder, whereat wearableArchitectView.load('http://your-server.com/arexperience.html') loads the file from a server.
wearableArchitectView.load('arexperience.html?myarg=1')
Location
Management of the location is important in location based augmented reality applications. Depending on the use-case location is used via GPS or network and may be updated every second or once in a while.
Although the SDKExamples project provides a basic implementation of a LocationProvider this is by far not the best location strategy available for Android.
Please use your own advanced location strategy implementation in case you have special requirements.
2D - 3D Modes
The Wikitude Epson SDK reacts automatically to changes in the display mode, which means that if the user switches from 2D to 3D mode the rendering is immedeately changed to 3D rendering mode.
For the 2D mode of the Epson Moverio BT-200 the same 960x540 pixel image is displayed on both displays while in 3D mode the image is split in half, the left half is displayed on the left eye and the right half is displayed on the right eye. The images for each eye in the 3D mode are 480x540 pixel stretched to fit the display. This means that if you want to show normal web content without AR objects you have to change the width to half the size. Every AR object is rendered by the Wikitude Epson SDK which means you don't have to change the width as this is handled internally. You can also force the rendering mode by using the Epson Moverio SDK. More information on the Epson Moverio SDK can be found in their Technical Information for Application Developer.